Growth conference
September 5 - 8
About
Tech1Media is under growing server expansion and improvements this week.
General Admission
$199
-
List all of the exciting benefits your customer will get if they purchase this tier.
-
What networking and learning opportunities are available to them at the conference?
-
What parts of the conference can they access?
-
Do they have access to any recorded programming?
-
What are their food, transportation, and accommodation options?
VIP
$449
-
List all of the exciting benefits your customer will get if they purchase this tier.
-
What networking and learning opportunities are available to them at the conference?
-
What parts of the conference can they access?
-
Do they have access to any recorded programming?
-
What are their food, transportation, and accommodation options?
Speaker panel
Add a short description of your speakers here. Why should your audience hear from them? Is there a theme they’ll all be covering in their talks? What makes them unique? Use this space to give the reader a sense of why these are the speakers you want to showcase.
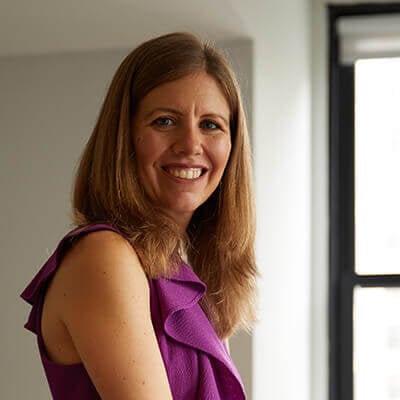

Abigail Johnson
CEO and Founder
Summarize your speaker's biography here. You can also add a sentence about their presentation topic.
Michelle Rodriguez
Chief Operating Officer
Summarize your speaker's biography here. You can also add a sentence about their presentation topic.
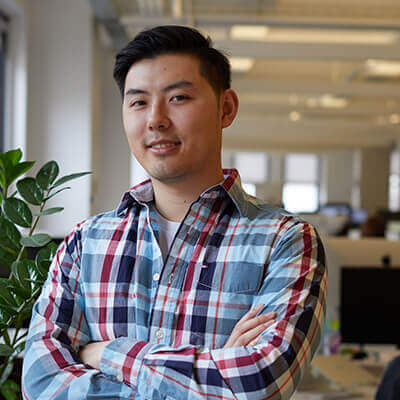

Stephen Kim
Chief Technology Officer
Summarize your speaker's biography here. You can also add a sentence about their presentation topic.
Sponsors




Testimonials
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.
“This is your chance to give social proof about how great your event is. Add testimonials that help people understand the value of your event.”
“This is your chance to give social proof about how great your event is. Add testimonials that help people understand the value of your event.”
“This is your chance to give social proof about how great your event is. Add testimonials that help people understand the value of your event.”
